Ceramics can exhibit very low wear rates compared with metals and they are being used increasingly in tribological situations they also retain similar properties up to high temperatures and they are very unreactive chemically so they will certainly find increasing use in hostile environments.
Ceramics wear rate.
Identifying the run in and steady state wear rates was a valuable step in processing the ceramic wear data and assessing its reliability.
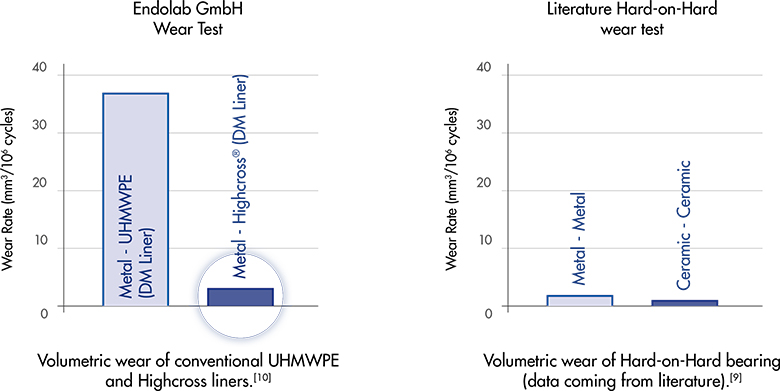
Ceramic on metal com bearings are considered to be a promising alternative to polyethylene based bearings or hard on hard bearings ceramic on ceramic coc and metal on metal mom.
The head wear rate alone is about 100 to 300 fold lower.
Thus the m m and c c thrs have demonstrated two to three orders of reduction in volumetric wear in the laboratory compared with the pe wear standard which helps to explain the excellent wear performance and.
Arnell in tribology and dynamics of engine and powertrain 2010.
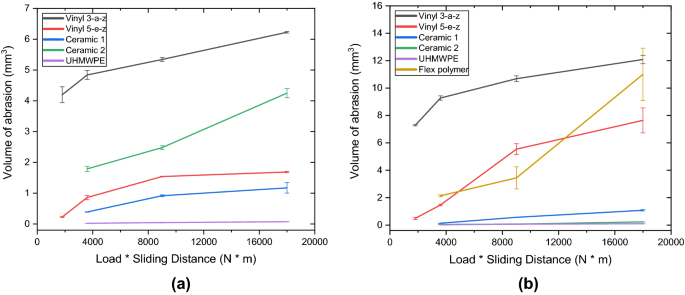
Wear of ceramics and cermets.
The friction and wear of oxide ceramics and silicon based ceramics in air at temperatures from room ambient to 900 c in a few cases to 1200 c were measured for a.
The friction and wear of ceramic ceramic and ceramic metal combinations in sliding contact the tribological characteristics of ceramics sliding on ceramics are compared to those of ceramics sliding on a nickel based turbine alloy.
The hip joint.
Hence the standard wear coefficient value obtained from a volume loss versus distance curve is a function of the sliding distance.
This may be related to limitations of wear measuring methods.
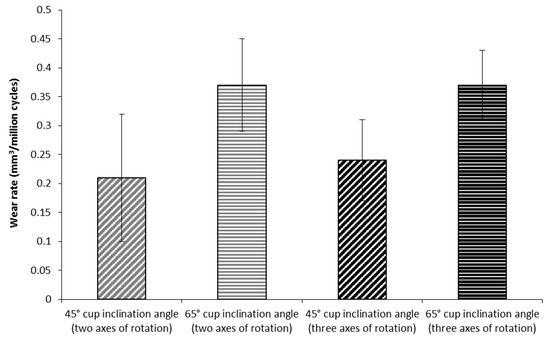
Although com shows lower wear rates than mom in vitro wear testing of com shows widely varying results.
The wear rate of al 2 o 3 13 tio 2 ceramic coating was evaluated by the wear volume and that of pins by weighing them before and after the tests.
The wear depth of pins was calculated by.